Understanding the High Frequency Transformer
In today’s world, electronic devices have become an integral part of our lives. From laptops to smartphones, and from power banks to chargers, everything requires an electronic transformer for proper functioning. One of the types of transformers that is commonly used in these devices is the high-frequency transformer.
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. It has two coils, a primary coil, and a secondary coil, which are wound around a magnetic core. The primary coil receives the electrical energy, which generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field then induces a voltage in the secondary coil, which can be used to power the electronic device.
A high-frequency transformer is a transformer that operates at high frequencies, typically between 20 kHz and 200 kHz. These transformers are used in electronic devices that require high-frequency switching, such as power inverters, switch-mode power supplies, and resonant converters. The high-frequency operation of these transformers results in several advantages, such as smaller size, lighter weight, and increased efficiency.
The design of a high-frequency transformer is critical to its performance. The core material used in the transformer must have a high permeability and low magnetic loss to minimize energy loss due to hysteresis and eddy currents. Common core materials used in high-frequency transformers include ferrite, powdered iron, and laminated steel.
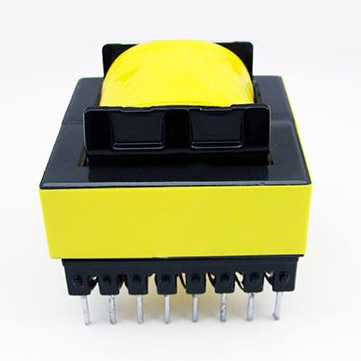
The winding configuration of the transformer is also essential. The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils determines the voltage ratio between the input and output of the transformer. The wire used for winding should have a high conductivity to minimize energy loss due to resistance. For high-frequency transformers, the wire used is typically thin, with a high number of turns.
Recommended article:What is the Difference Between SWA and Armoured Cable?
Understanding the Difference Between SWA and Armoured Cable
SWA Cable VS Armoured Cable
What Are the Advantages of Using an SMPS Transformer?
How to Use an Electric Blanket Switch Safely?
Advantages of Dry Type Power Transformers
What are the types of power resistors?
One of the primary advantages of high-frequency transformers is their small size and light weight. This is because the higher frequency allows for smaller core sizes and thinner wire. Additionally, high-frequency transformers are more efficient than low-frequency transformers. This is because the energy loss due to resistance is lower at higher frequencies, and the magnetic core losses are minimized due to the use of specialized core materials.
Another advantage of high-frequency transformers is their ability to operate at high power levels. This is because the higher frequency allows for faster switching times, which results in lower energy loss and higher efficiency. High-frequency transformers are used in applications that require high power levels, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial equipment.
Despite their advantages, high-frequency transformers have some limitations. The primary limitation is the higher cost of the specialized core materials used in their construction. Additionally, the high-frequency operation of the transformer can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can affect the performance of other electronic devices. To mitigate this, EMI filters are often used in conjunction with high-frequency transformers.
In conclusion, the high-frequency transformer is a critical component of many electronic devices. Its small size, light weight, and high efficiency make it an ideal choice for applications that require high-frequency switching and high power levels. However, the design and construction of high-frequency transformers must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and minimize energy loss. As electronic devices continue to evolve, the demand for high-frequency transformers will only continue to grow.
Understanding the Difference Between Electrolytic Capacitors and Normal Capacitors
Understanding the Rochchip Android Linux AIOT Core Board
Understanding the Basics and Key Features of Car Starter Battery
Understanding the Benefits of Residential Energy Storage Solutions
Advantages of Thick Film Chip Resistors
Car Stop-Start Battery: Paving the Way for Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Sustainability
What are Applications of Liquid Crystal Light Valves?
- 0

- 1489
- 0
- 0

- 1433
- 0
- 0








